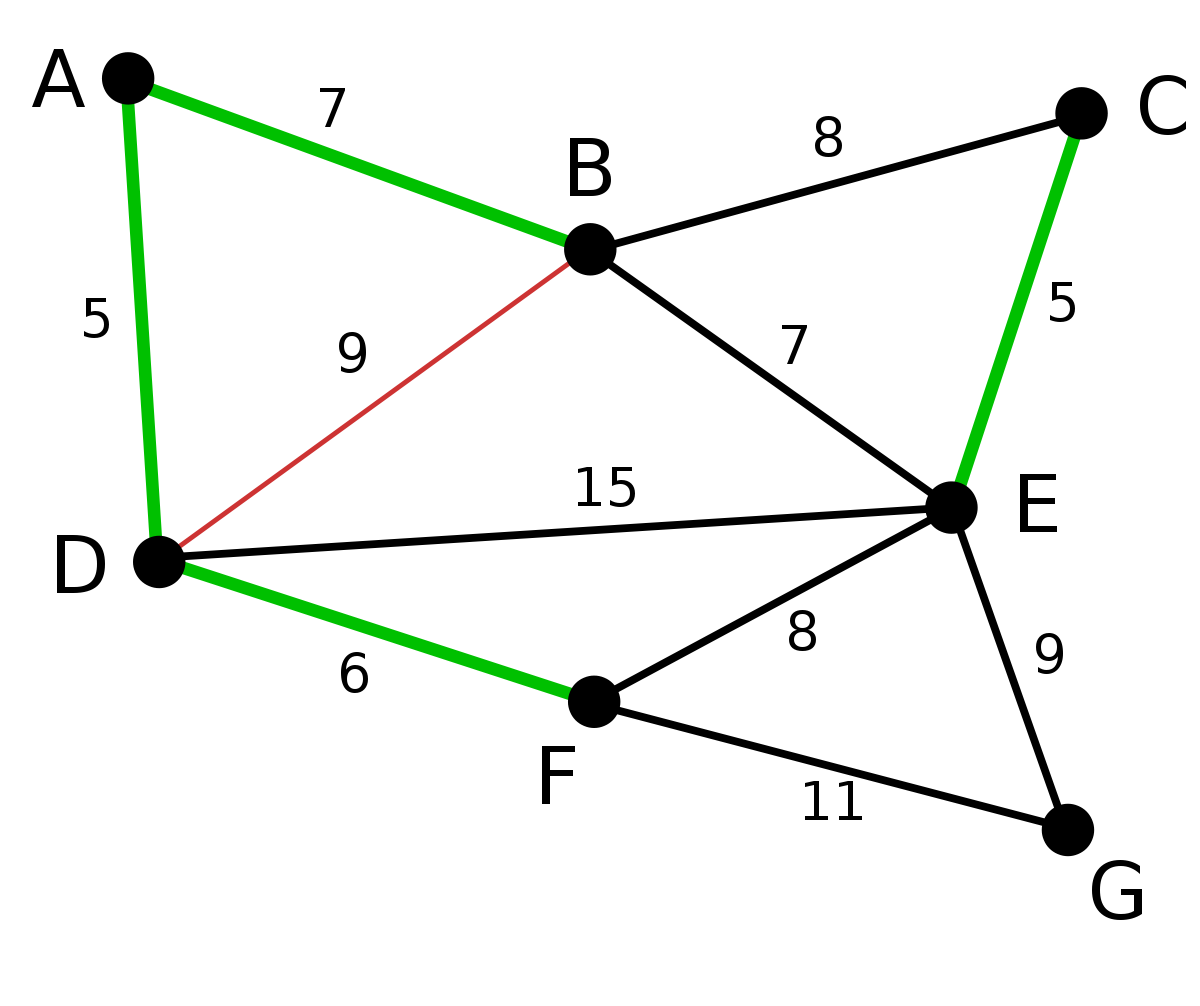
: 그래프 구조에서 간선들의 합이 최소가 되는 트리를 구현하기 위해 나온 알고리즘
1. MST를 Prim 알고리즘으로 구현하기 (인접행렬)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/* MST : 프림 알고리즘 이용 */
public class MST2_Prim {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine().trim());
int[][] input = new int[N][N]; // 정점 크기 만큼 인접행렬
boolean[] visited = new boolean[N]; // 신장 트리 선택 여부 채킹
int[] minEdge = new int[N]; // 신장 트리에 포함된 정점으로부터 자신과 연결하는 간선 비용 중 최소비용
// -- 인접행렬 input 초기화
StringTokenizer tokens;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
tokens = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine(), " ");
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
input[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(tokens.nextToken());
}
// 최소값을 위해서 정수형 최대값으로 초기화
minEdge[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// --
int minVertex, min; // 최소정점, 최소 정점의 간선비용
int result = 0; // MST 비용
minEdge[0] = 0; // 임의의 시작점 비용으로 초기화 설정
// -- 1단계 정점중심 해결: 모든 정점수만큼 반복하면서 모든 정점을 연결
for (int c = 0; c < N; c++) {
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 초기값을 최대값으로 설정
minVertex = 0; // 임의정점: 0
// -- N 개의 정점 반복하면서 가장 유리한(최소비용) 정점 선택
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
if (!visited[i] && min > minEdge[i]) {
min = minEdge[i]; // 현재 간선 비용이 최소이니 갱신
minVertex = i; // 현재 정점으로 최소 정점(신장트리) 설정
}
}
visited[minVertex] = true; // 선택된 정점으로 신장트리 포함시킴
result += min; // 선택된 정점의 비용을 mst 누적
// -- 2단계:
// 선택된 최소비용 정점과 신장트리 구성에 포함되지 않는 타정점으로의 최소비용 갱신
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (!visited[i] // 해당 정점이 신장트리에 포함되어 있지 않고
&& input[minVertex][i] != 0 // 인접해있는 정점이고
&& minEdge[i] > input[minVertex][i]) {
// i에 해당하는 정점이 다른 정점에서 자신한테 연결하려할 때 간선의 최소비용이 크다면 갱신
minEdge[i] = input[minVertex][i]; // 가장 유리한 비용으로 갱신
}
}
}
// 모든 정점이 연결한 간선 비용 mst 출력
System.out.println(result);
}
}
2. MST를 Prim 알고리즘으로 구현하기 (인접리스트, Heap 이용)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class PrimTest {
static class Node {
int vertex, weight;
Node next;
public Node(int vertex, int weight, Node next) {
this.vertex = vertex;
this.weight = weight;
this.next = next;
}
}
static class Vertex{
int no, weight;
public Vertex(int no, int weight) {
this.no = no;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
int V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
Node[] adjList = new Node[V];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int weight = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
adjList[from] = new Node(to, weight, adjList[from]);
adjList[to] = new Node(from, weight, adjList[to]);
}
// 프림 알고리즘에 필요한 자료 구조
int[] minEdge = new int[V];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
Arrays.fill(minEdge, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 1. 임의의 시작점 처리, 0 변정점을 신장 트리구성의 시작점
minEdge[0] = 0;
int result = 0; // 최소 신장트리 비용 누적
PriorityQueue<Vertex> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v1.weight - v2.weight);
pq.offer(new Vertex(0, minEdge[0]));
int cnt = 0;
while(true) {
Vertex minVertex = pq.poll();
if(visited[minVertex.no]) continue;
// step 2. 신장트리에 추가
visited[minVertex.no] = true;
result += minVertex.weight;
if(++cnt == V) break;
// step 3. 신장트리에 새롭게 추가되는 정점과포함되지 않은 정점들의 기존 최소비용과 비교해서 갱신
for (Node temp = adjList[minVertex.no]; temp != null; temp = temp.next) {
if(!visited[temp.vertex] && minEdge[temp.vertex] > temp.weight) {
minEdge[temp.vertex] = temp.weight;
pq.offer(new Vertex(temp.vertex, temp.weight));
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
3. MST를 Kruskal 알고리즘으로 구현하기 (인접리스트)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class MST_Kruskal {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{ // 간선리스트 클래스 생성
int from, to, weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
}
static int V, E;
static int[] parent;
static long ans;
static List<Edge> edgeList;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int T = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
for (int test_case = 1; test_case <= T; test_case++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
edgeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
edgeList.add(new Edge(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()), Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()), Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())));
}
parent = new int[V + 1]; // 서로소 집합
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
Collections.sort(edgeList);
ans = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for(Edge e: edgeList) {
if(union(e.from, e.to)) {
ans += e.weight;
if(++cnt == V - 1) break;
}
}
sb.append("#").append(test_case).append(" ").append(ans).append("\n");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
private static boolean union(int from, int to) { // 합치기
int fRoot = find(from);
int tRoot = find(to);
if(fRoot == tRoot) {
return false;
}
parent[fRoot] = tRoot;
return true;
}
private static int find(int v) {
if(parent[v] == v) return v;
return parent[v] = find(parent[v]);
}
}
✓ V(정점의 개수)가 1000이고 E(간선의 개수)가 V² 일 때 MST를 구하려면?
- 어떤 알고리즘(Kruskal, Prim) &어떤 자료구조(인접행렬, 인접리스트) 를 사용해야 할까?
