출처 :
DFS와 BFS는 그래프 자료 구조를 이용한다.
DFS : 말 그대로, 방향 그래프에서는 시작 노드부터 방향을 따라 깊숙히 탐색하는 것이다.
BFS : 노드의 이웃 노드(노드에 연결되어 있는 노드)를 순서대로 탐색하는 것이다.
아래의 방향 그래프에서 노드 a를 시작점으로 그래프를 DFS 방식과 BFS 방식으로 순회해보자.
🍍 { 깊이 우선 순회, DFS : a,b,d,.. }
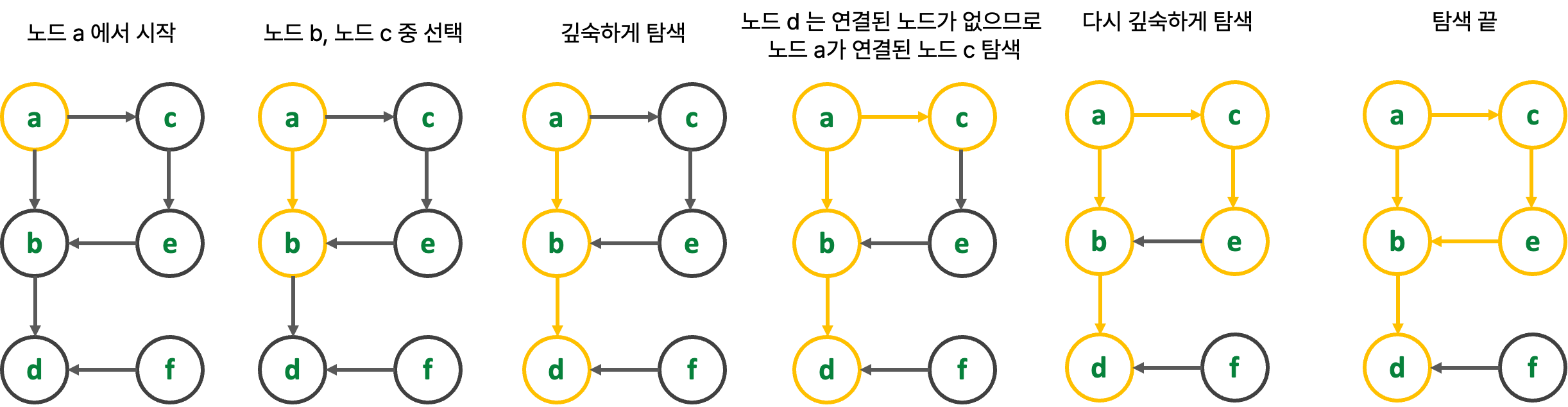
🎀 { 넓이 우선 순회, BFS : a,b,c,.. }
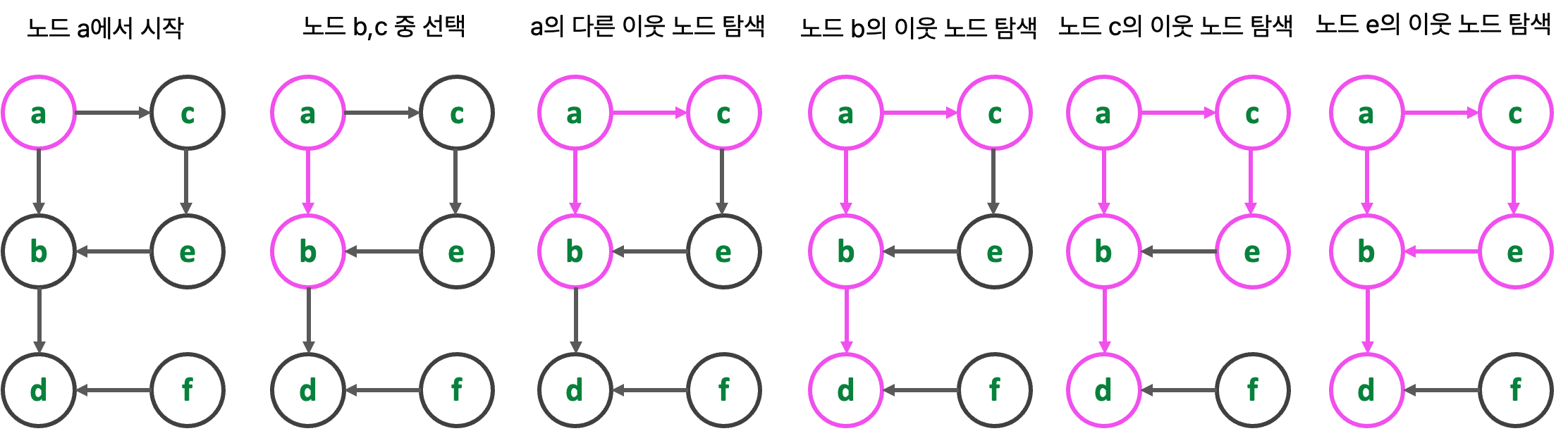
확실히 탐색 순서에서 차이가 보인다. 하지만 아래의 그림을 본다면 차이를 더욱 한눈에 알아볼 수 있다.
DFS는 시작점에서 아주 깊숙하게 탐색을 하고, BFS는 인접해 있는 노드를 중심으로 탐색을 한다.
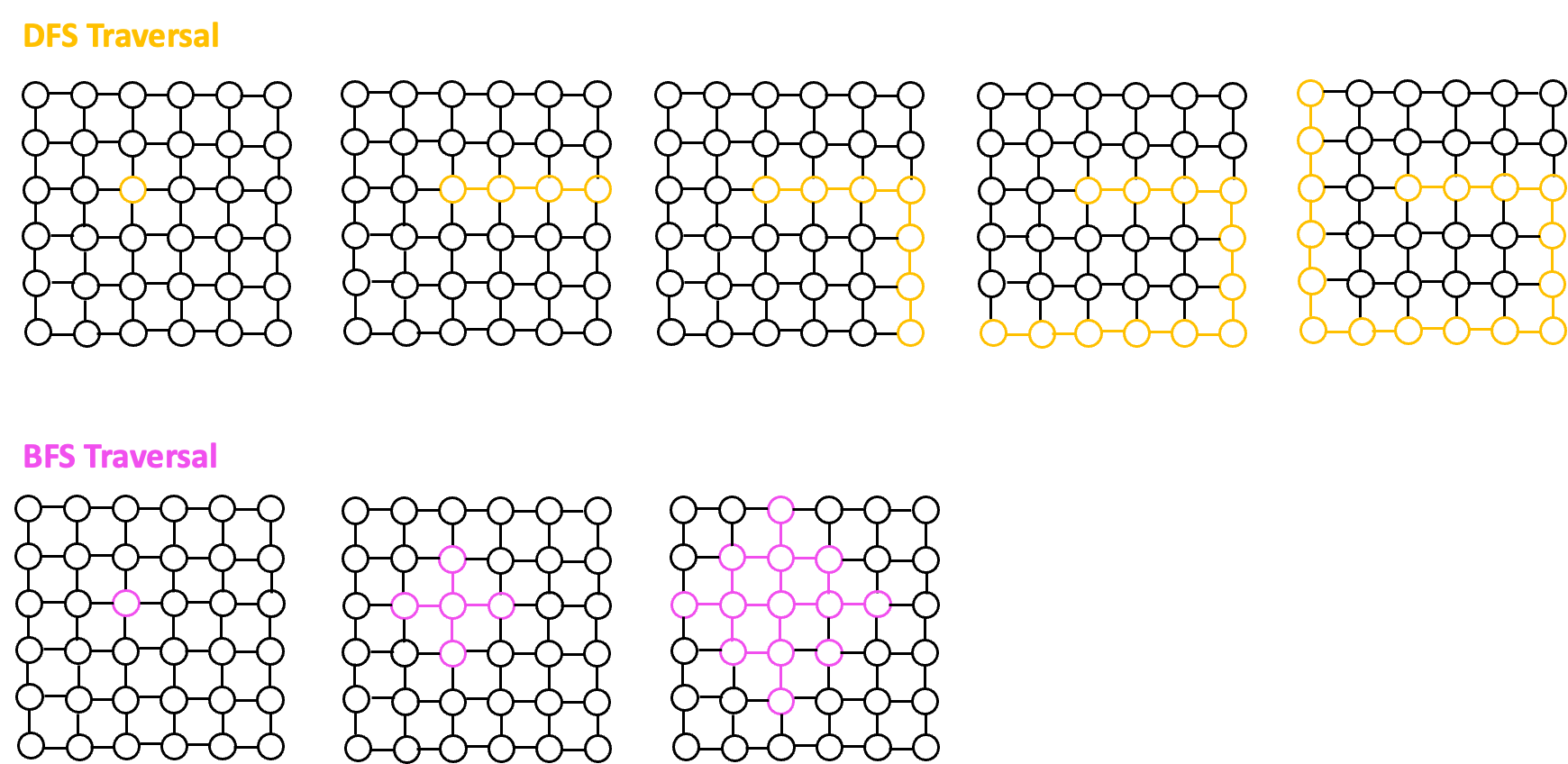
DFS는 Stack(LIFO)으로, BFS는 Queue(FIFO)로 구현한다.
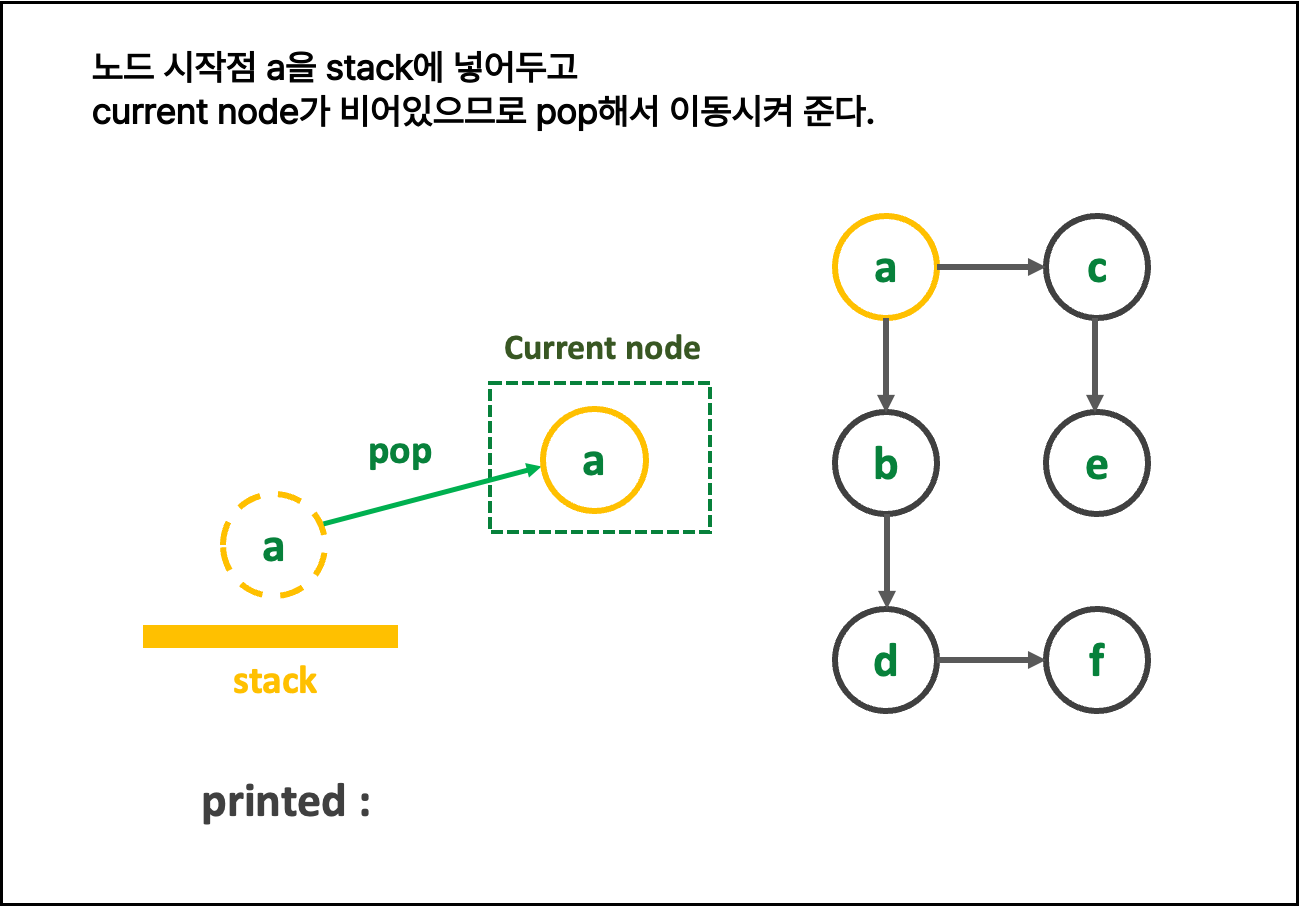
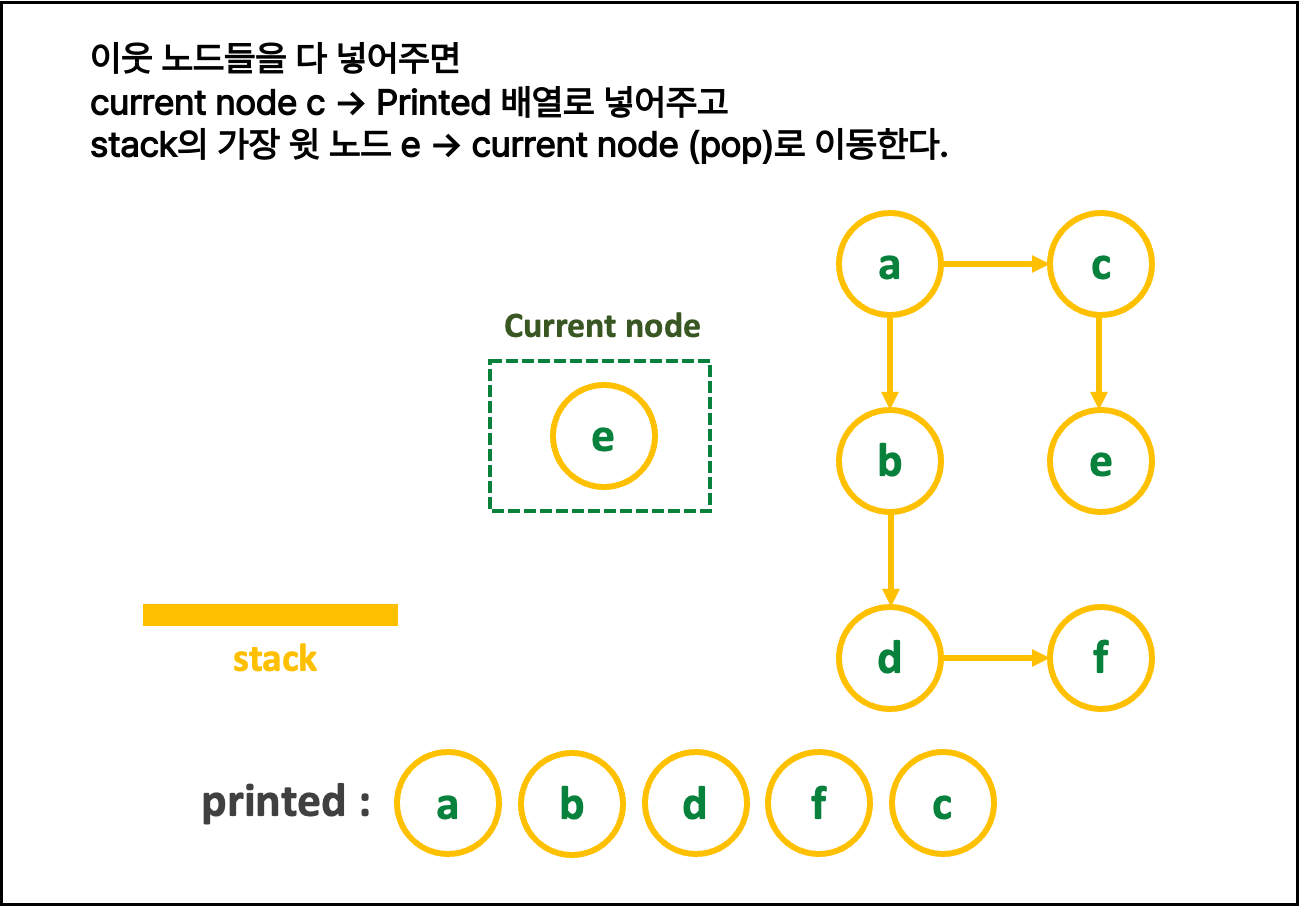
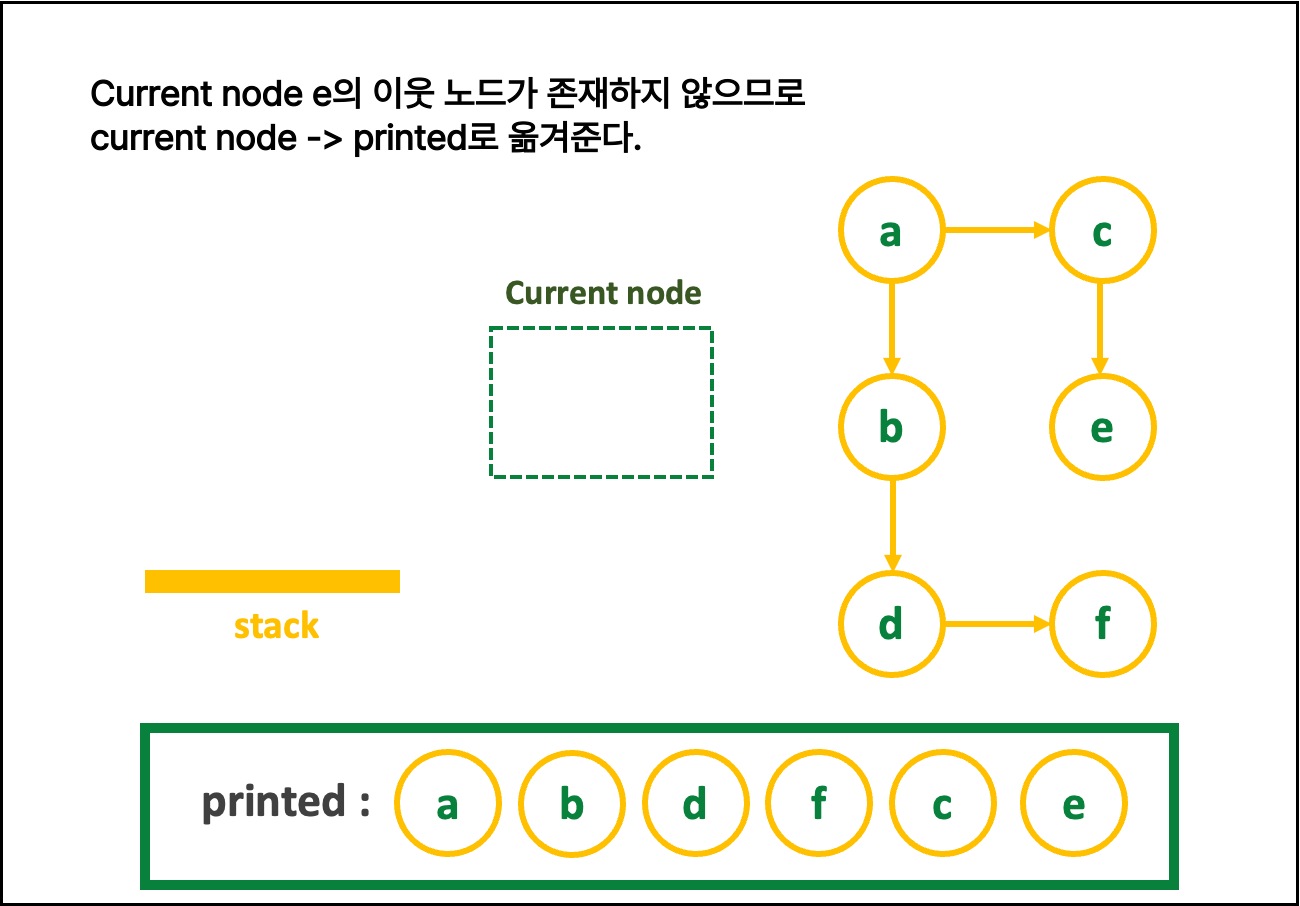
🍍 { DFS 알고리즘 설명 (스택) }
1. 친절한 그림 설명 : 그림을 클릭해 > 를 눌러 보세여
일일히 다 파워포인트로 만든 것이니, 몰래 가져가면 안됨
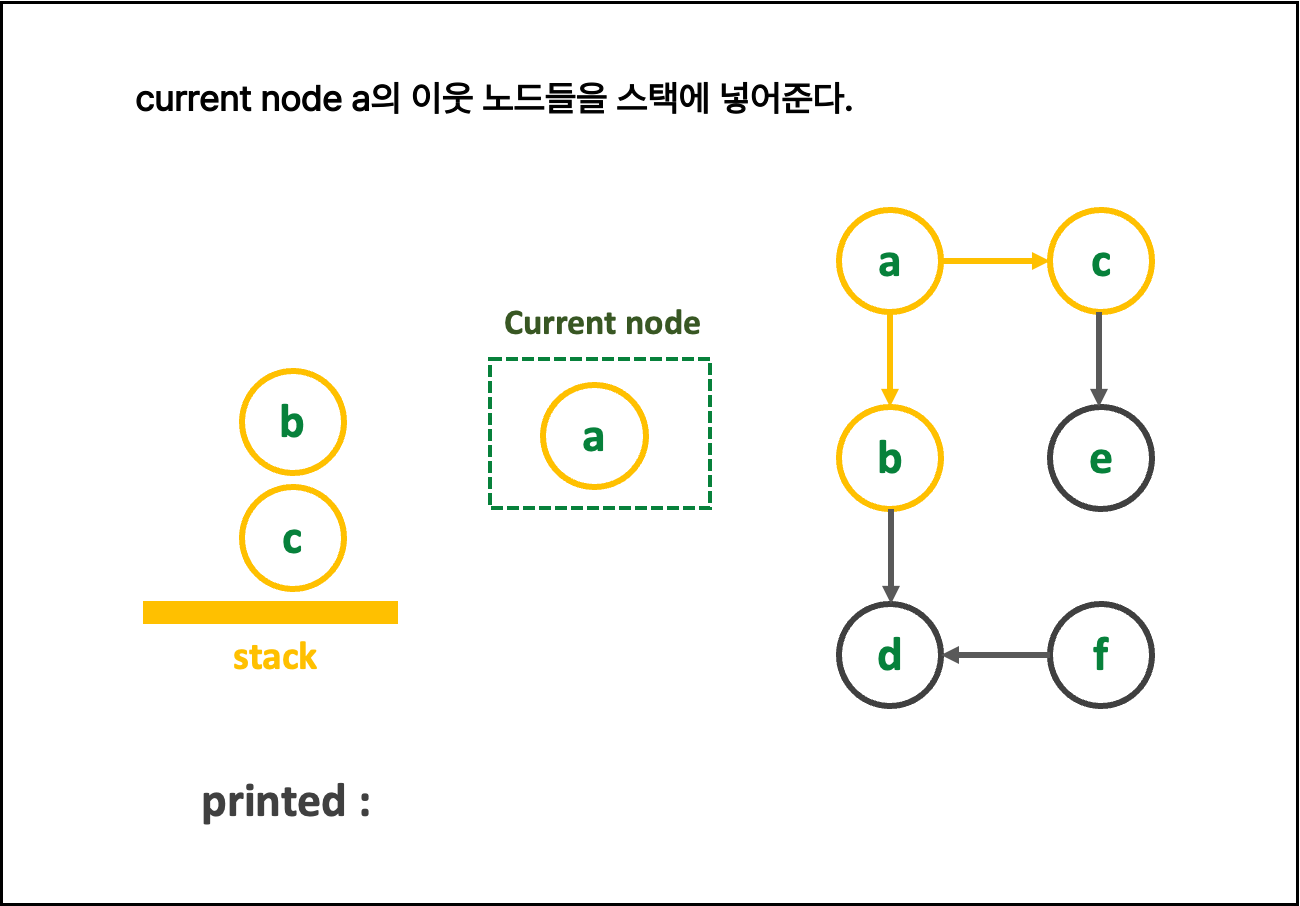
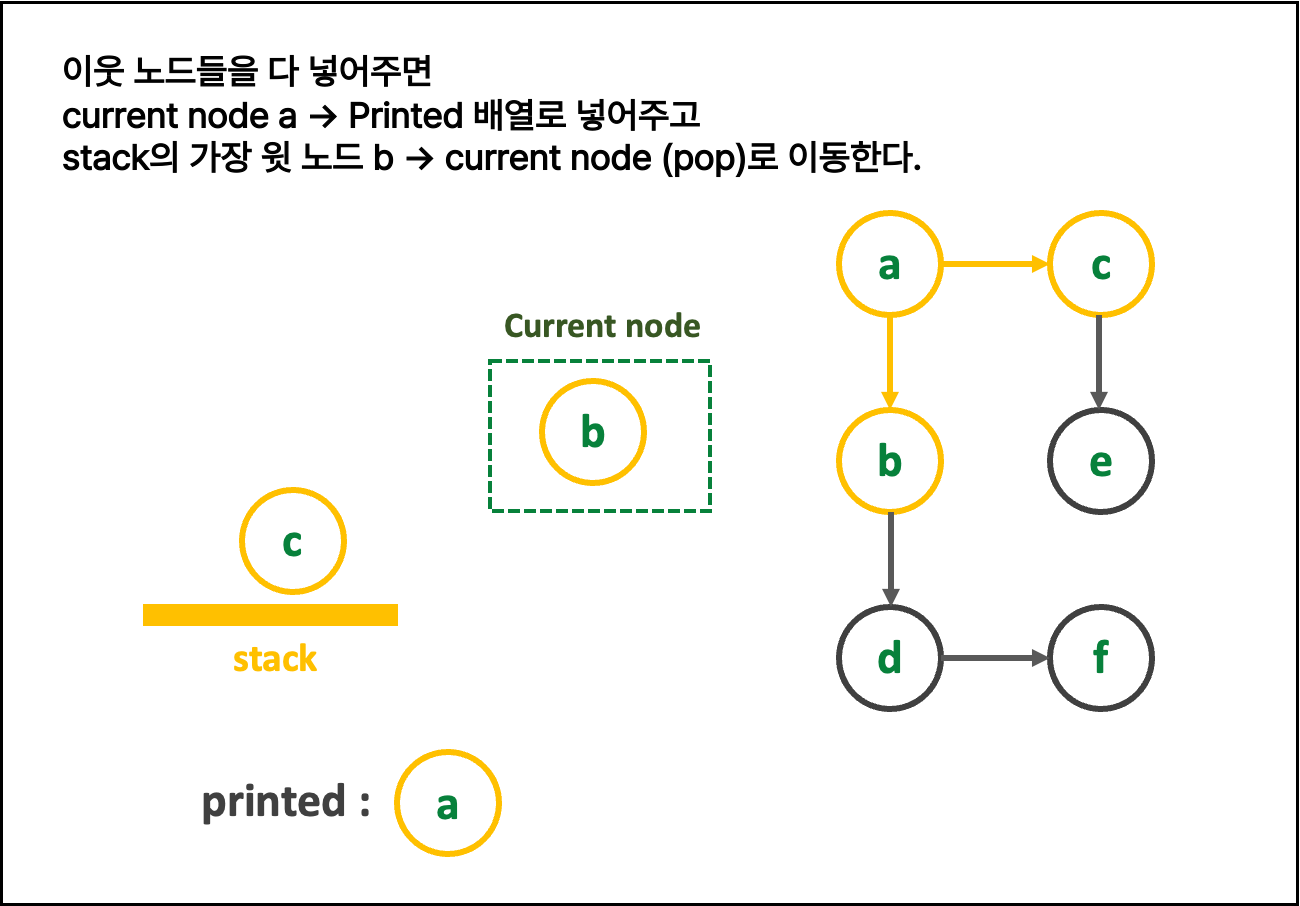
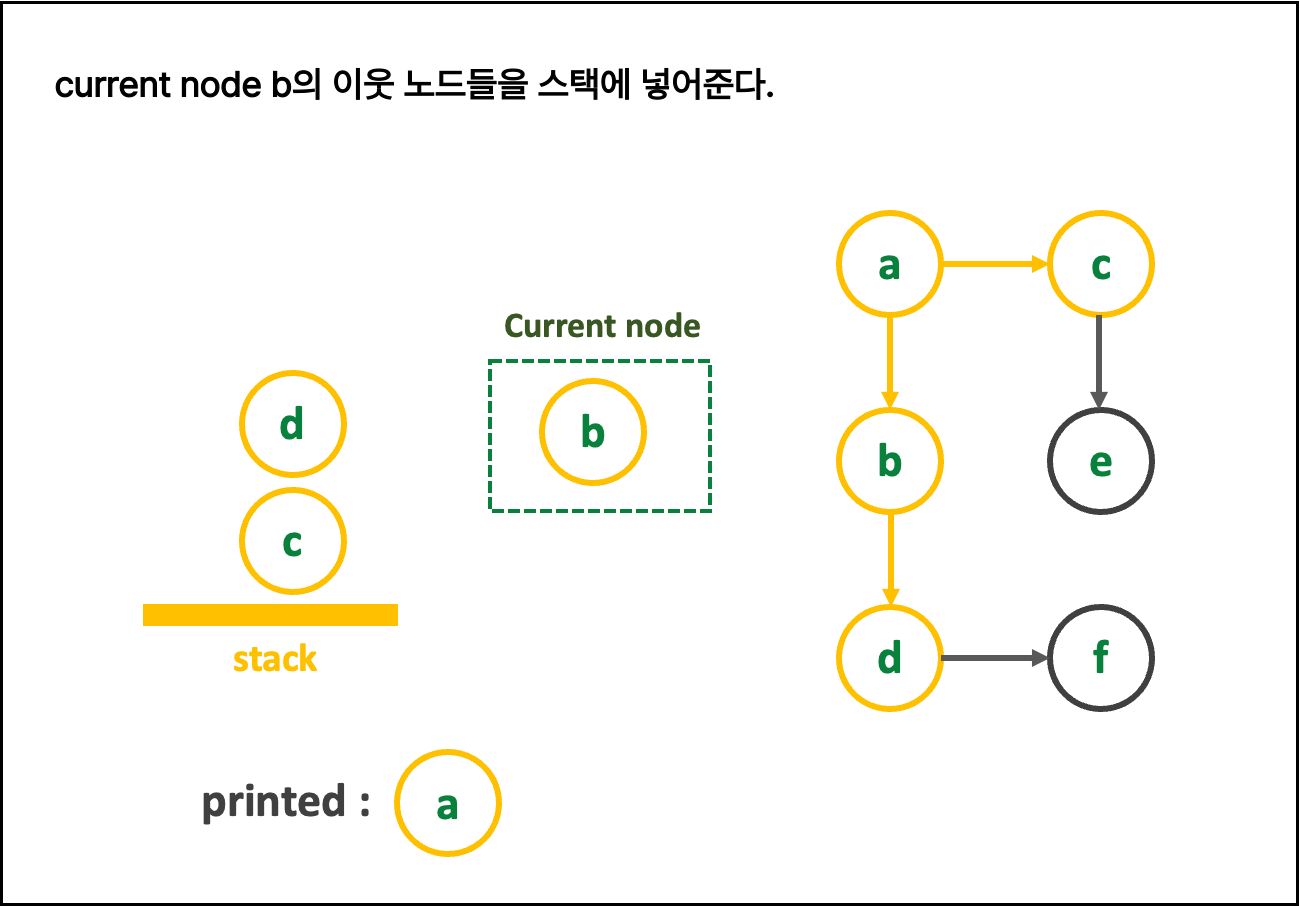
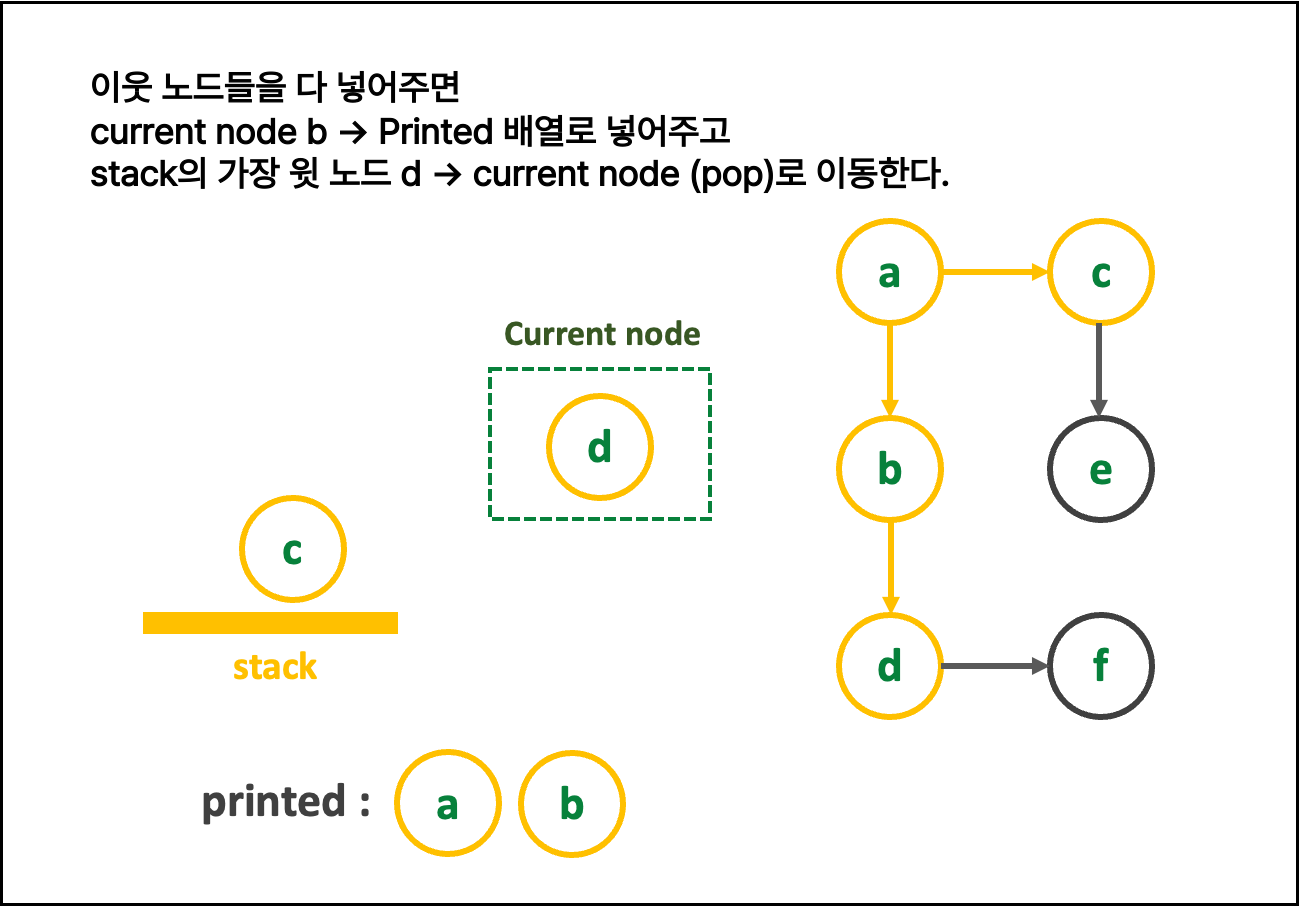
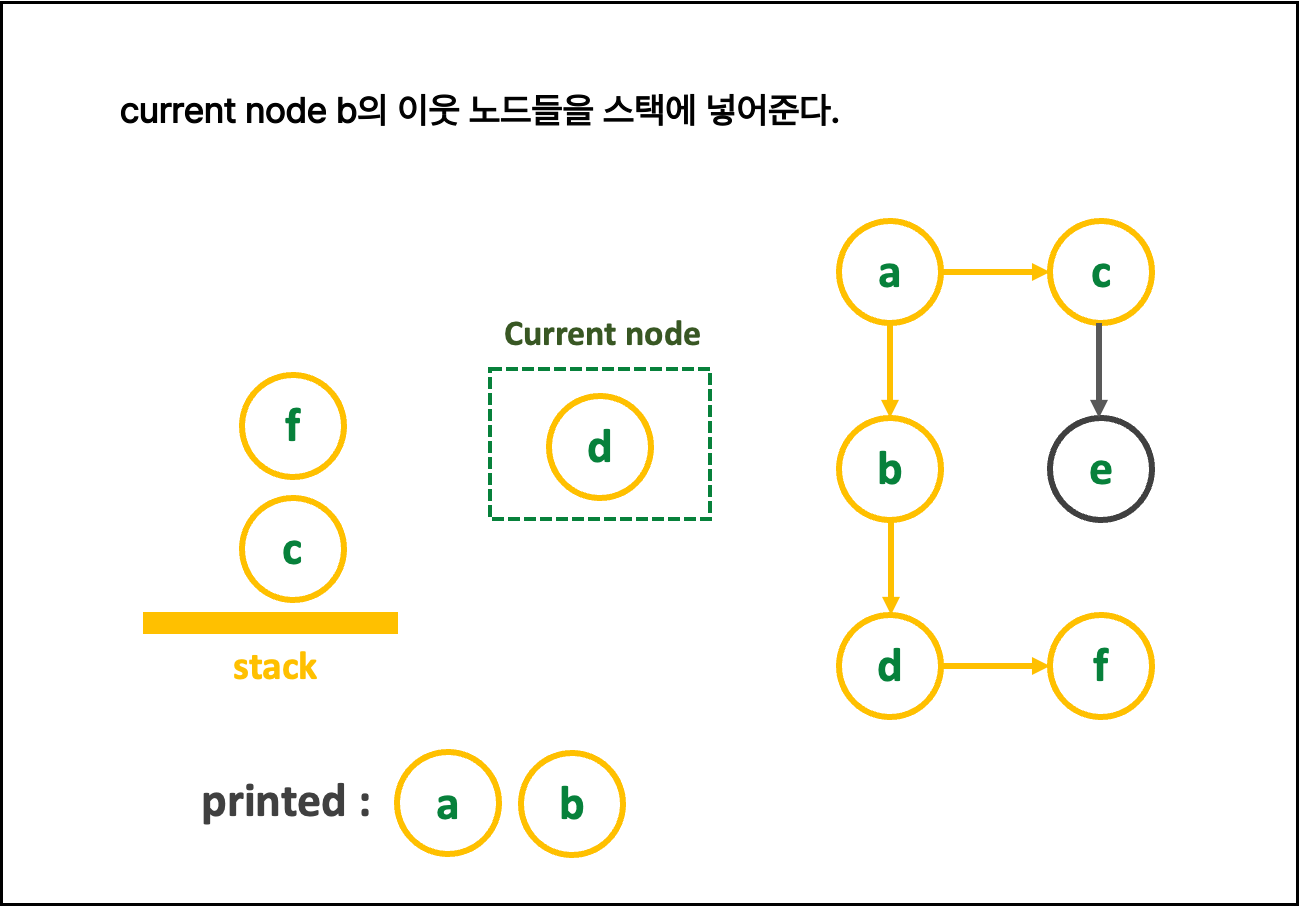
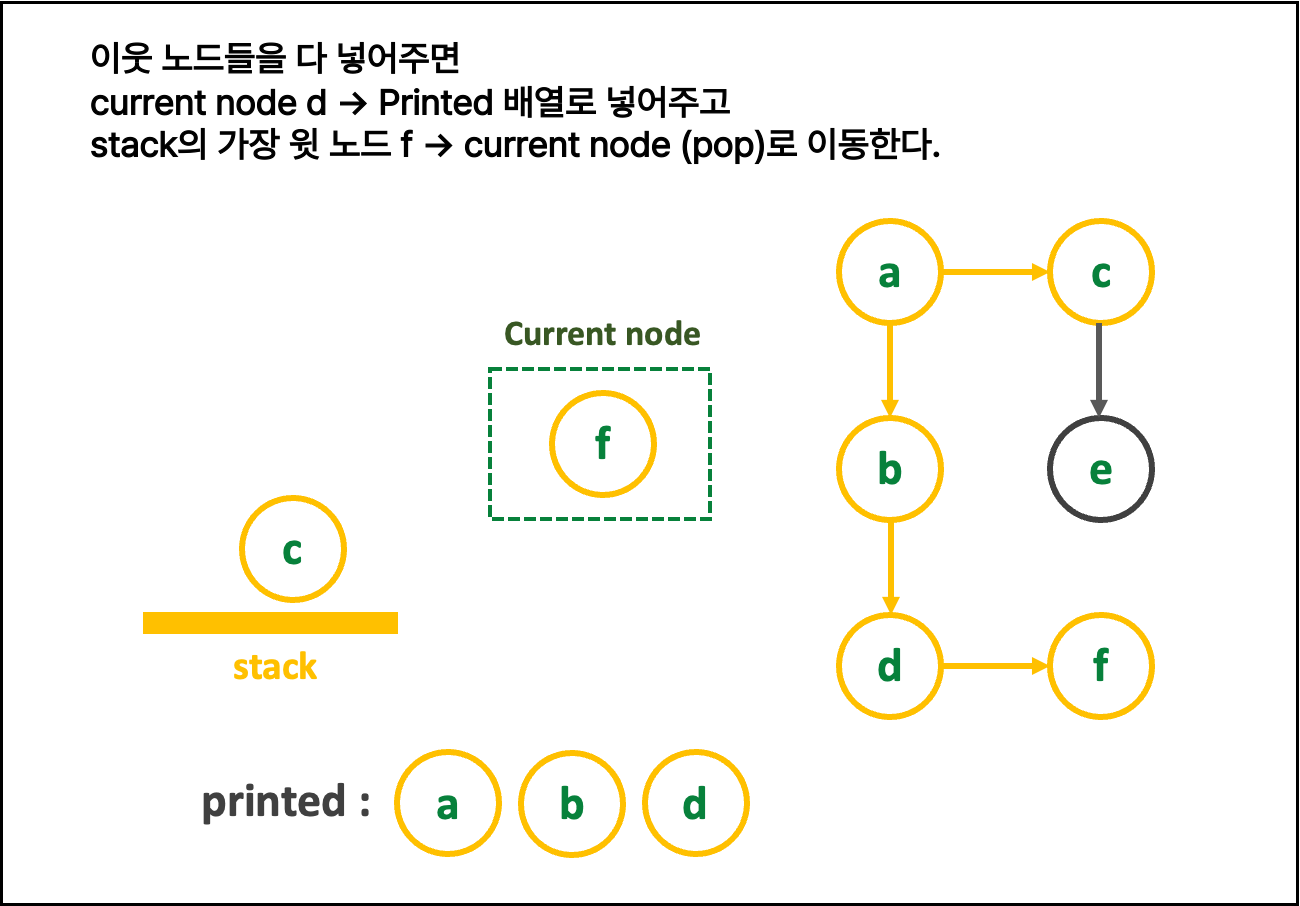
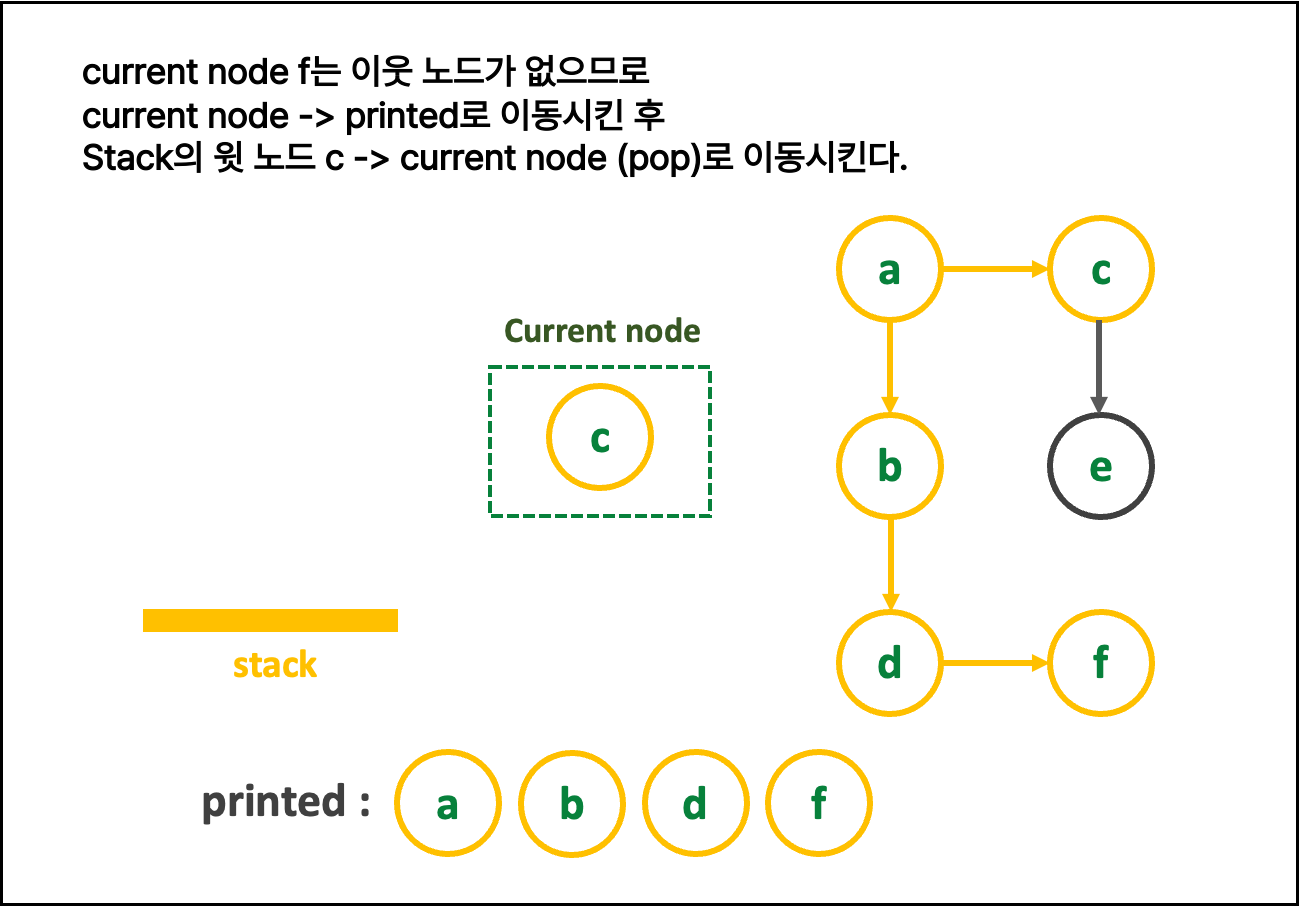
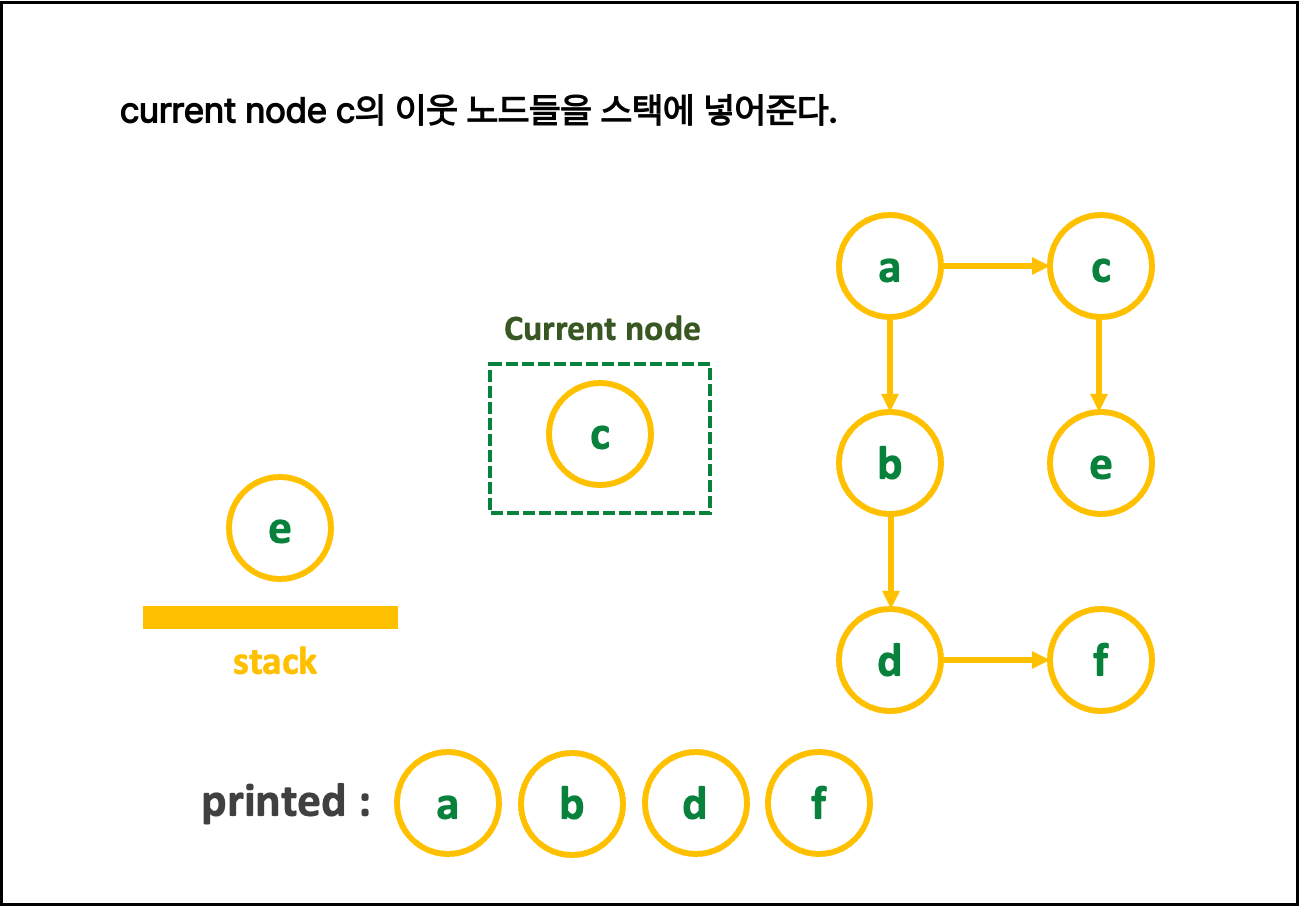
2. 글로 쓰는 로직
👇🏻 실패한 로직이다.
def DFS(node : 순회 시작 노드)
필요한 자료구조 : stack [], printed array[], current_node = None
[ while(True) 반복문 ]
1. stack == empty일 경우, 반복문을 종료한다.
2. current_node == None 일 경우, current_node= stack.pop()(시작 노드)로 설정
3. stack 에 current_node의 neighbors를 삽입
4. printed에 current_node를 append(추가)
5. current_node = stack.pop()으로 해준다.
이 로직을 바탕으로 아래와 같이 코드를 짰는데 stack이 어느 순간 empty인 상태가 되는 것을 발견했다.
# 에러코드
def findNeighbor(graph, current_node, stack):
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
stack.append(neighbor)
return stack
def dfsTraversal(graph, start_node):
stack = []
printed = []
stack.append(start_node)
current_node = None
while true:
if len(stack) == 0:
print("stack is empty")
break
if current_node == None:
current_node = stack.pop()
printed.append(current_node)
stack = findNeighbor(graph, current_node, stack)
current_node = stack.pop()
return printed
graph = {'a':[],'b':[],'c':[],'d':[],'e':[],'f':[]}
edges = [['a','c'],['a','b'],['b','d'],['c','e'],['d','f']]
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
print(dfsTraversal(graph, 'a')) # 출력 결과 : ['a', 'b', 'd', 'f']
current_node에 노드 c가 있을 때에 뭔가 문제가 일어났는데 혹시 아는 사람 댓글좀..ㅎ
✓ 다시 짠 로직
def DFS(graph : 그래프, start_node : 순회 시작 노드)
필요한 자료구조 : stack [], printed array[], current_node
1. stack에 start_node 넣어주기
[ while(True) 반복문 : len(stack) == 0 일 경우 종료 ]
2. current.node = stack.pop() 으로 설정
3. stack 에 current_node의 neighbors를 삽입
4. printed에 current_node를 append(추가)
3. 코드 구현
def dfsTraversal(graph, start_node):
stack = []
printed = []
stack.append(start_node)
while len(stack) != 0:
current_node = stack.pop()
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
stack.append(neighbor)
printed.append(current_node)
return printed
graph = {'a':[],'b':[],'c':[],'d':[],'e':[],'f':[]}
edges = [['a','c'],['a','b'],['b','d'],['c','e'],['d','f']]
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
print(dfsTraversal(graph, 'a')) # 출력 결과 ['a', 'b', 'd', 'f', 'c', 'e']
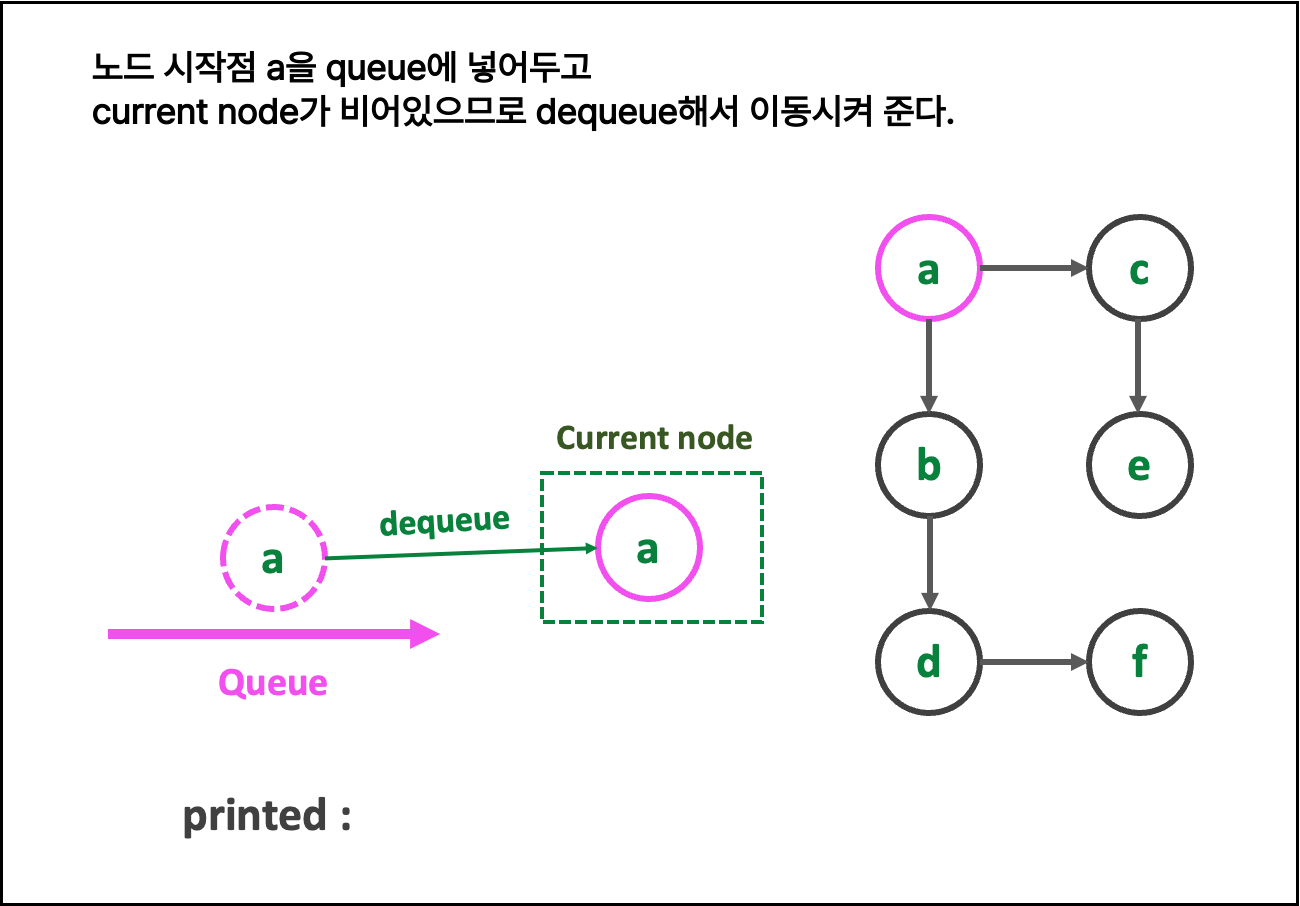
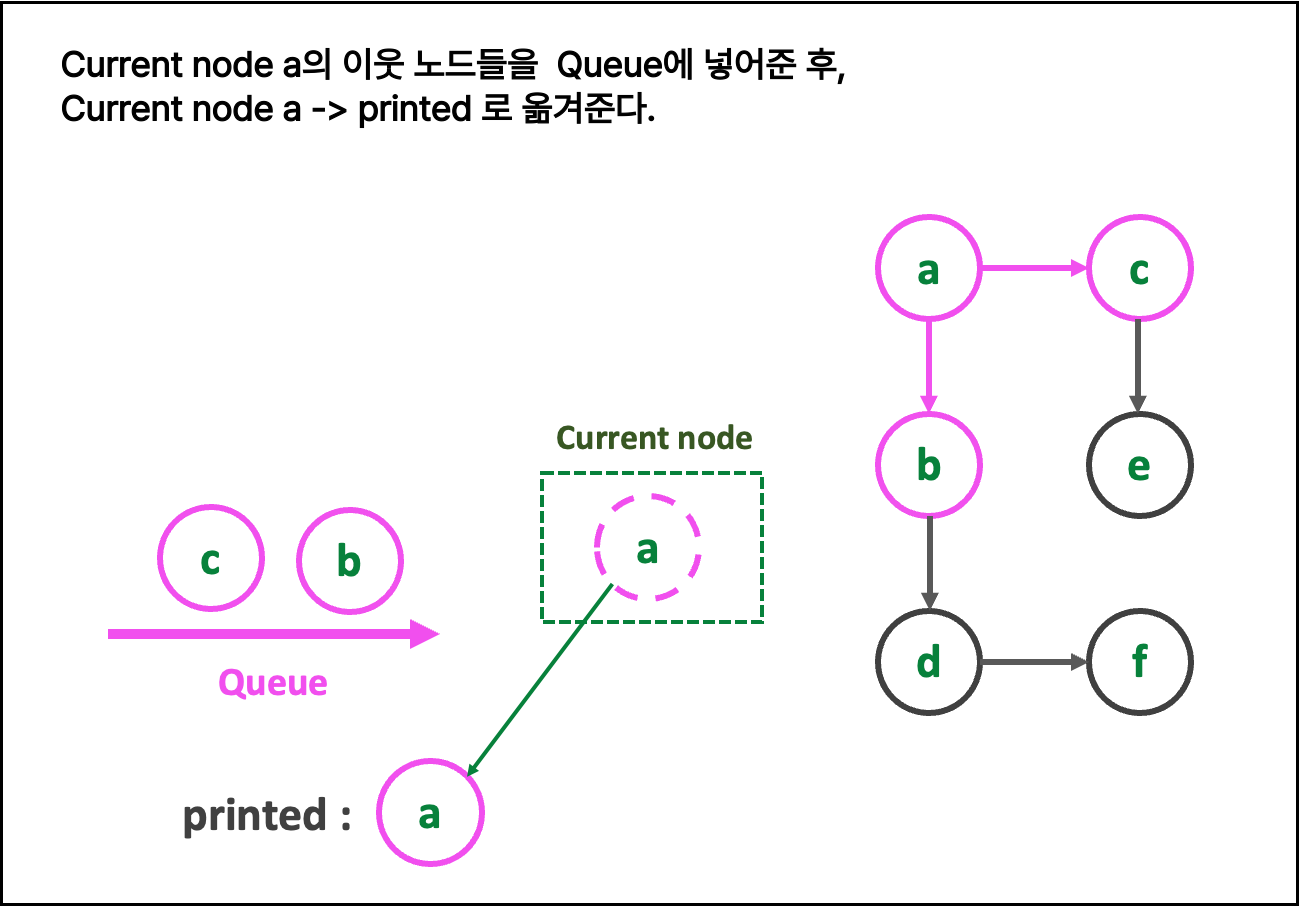
🎀 { BFS 알고리즘 (큐) }
1. 친절한 그림 설명 : 그림을 클릭해 > 로 확인하세여
일일히 다 파워포인트로 만든 것이니, 몰래 가져가면 안됨
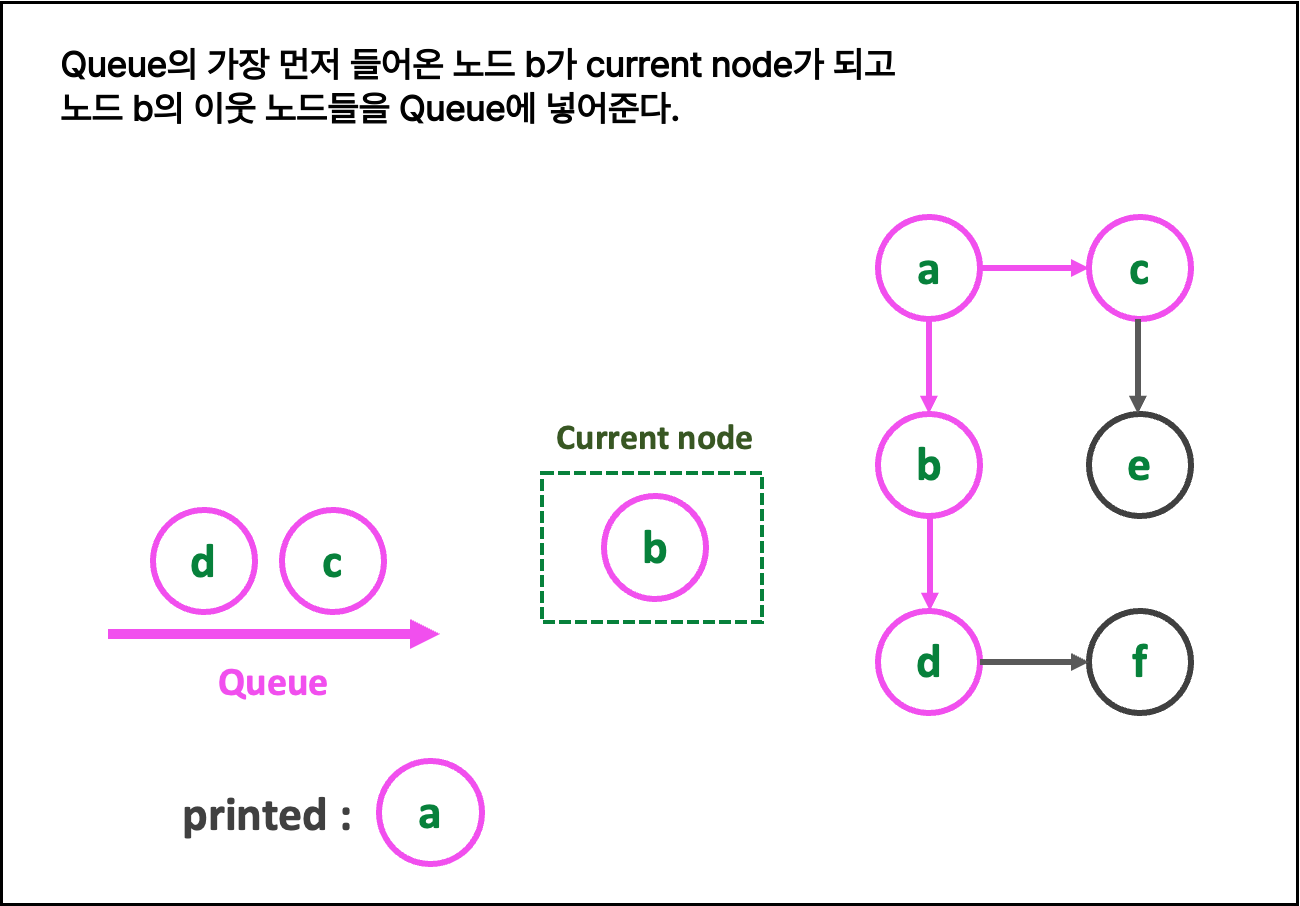
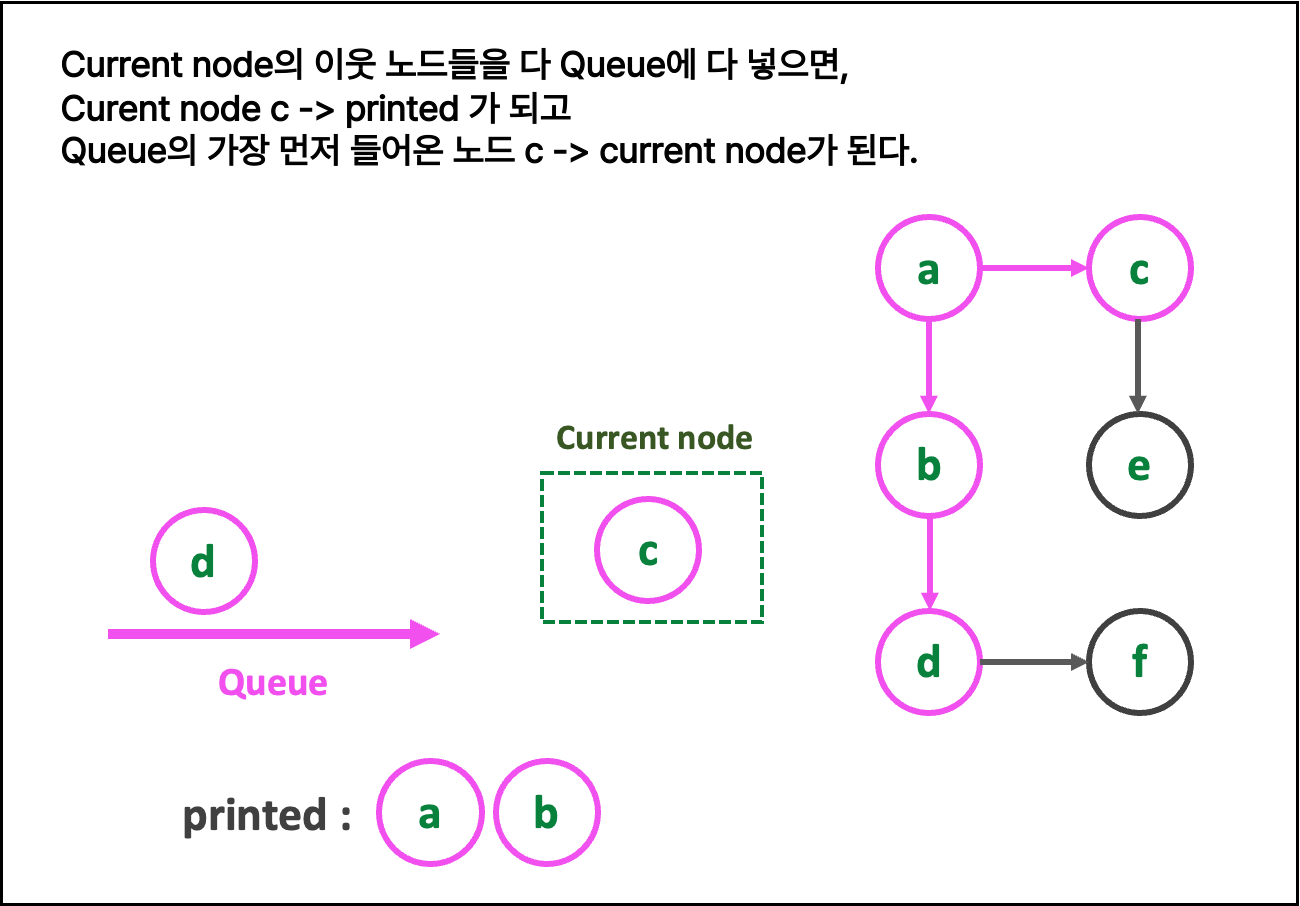
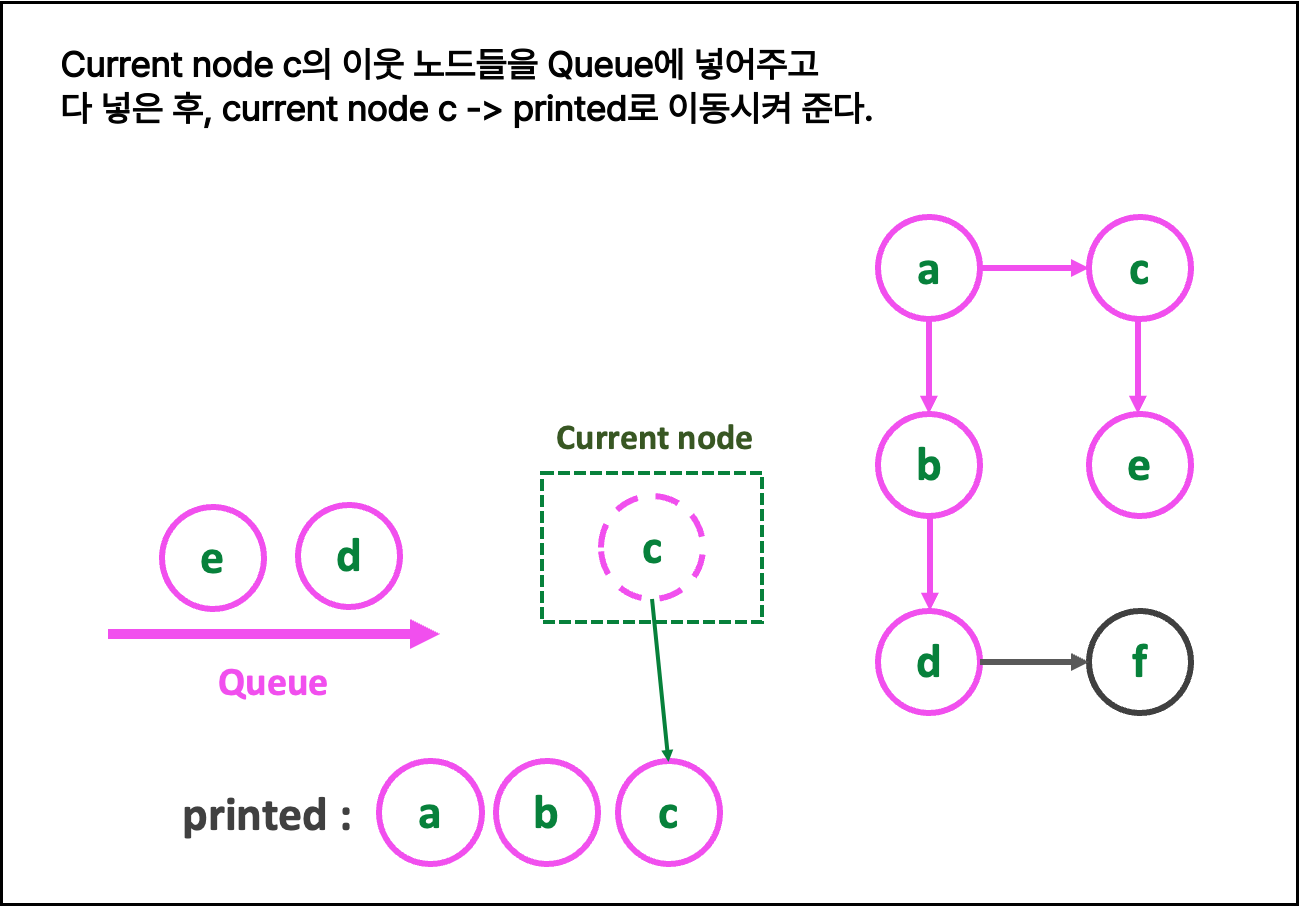
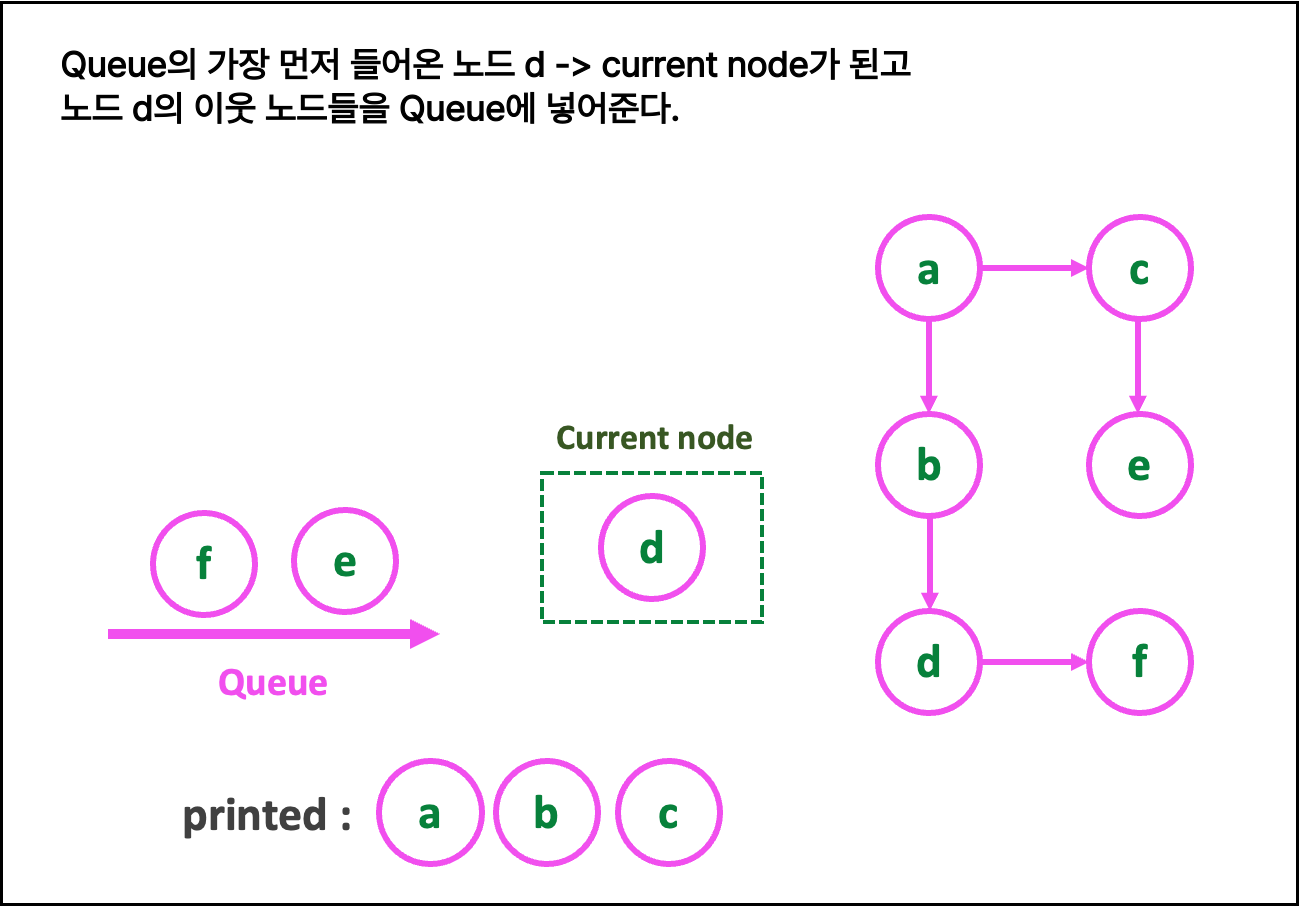
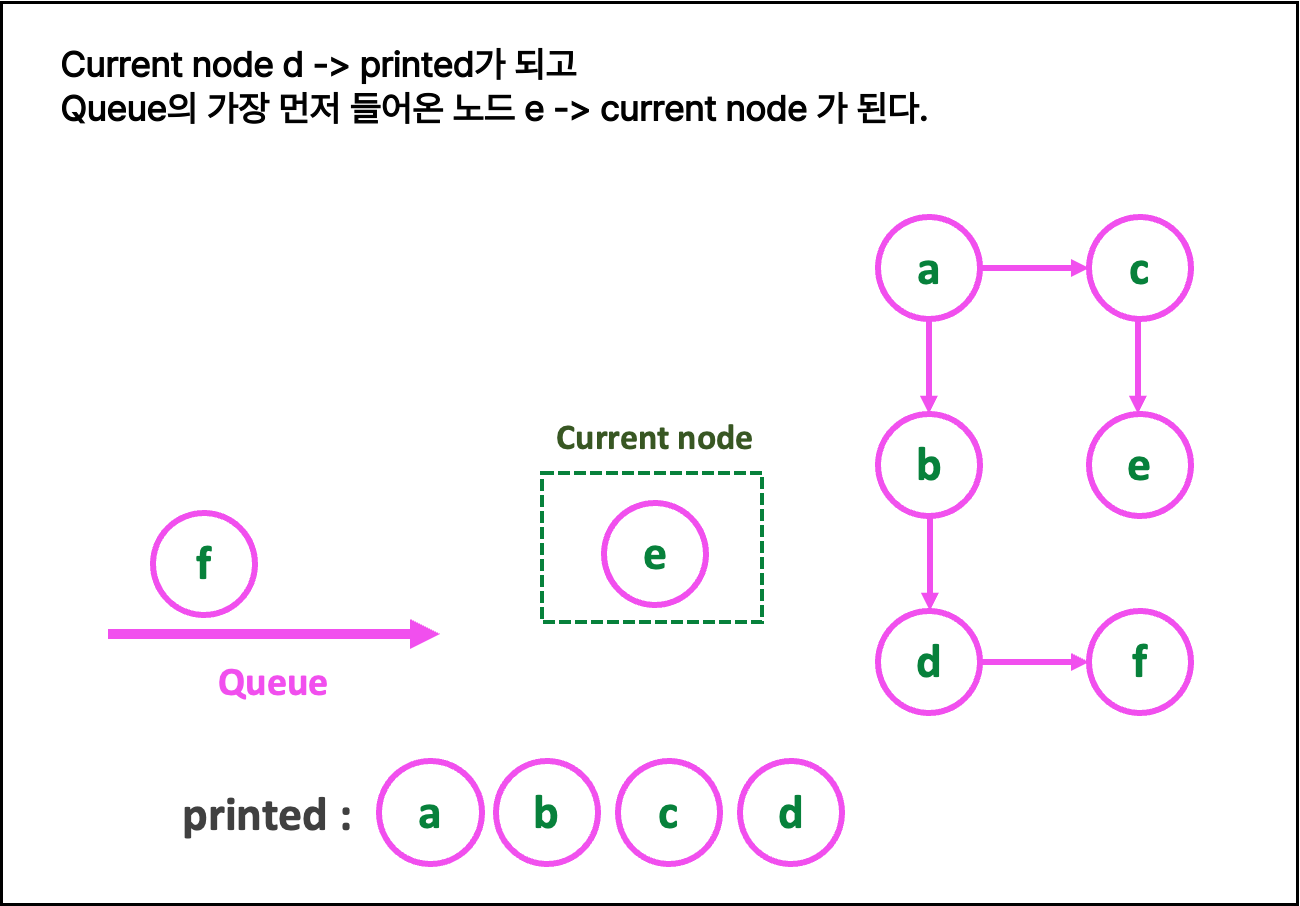
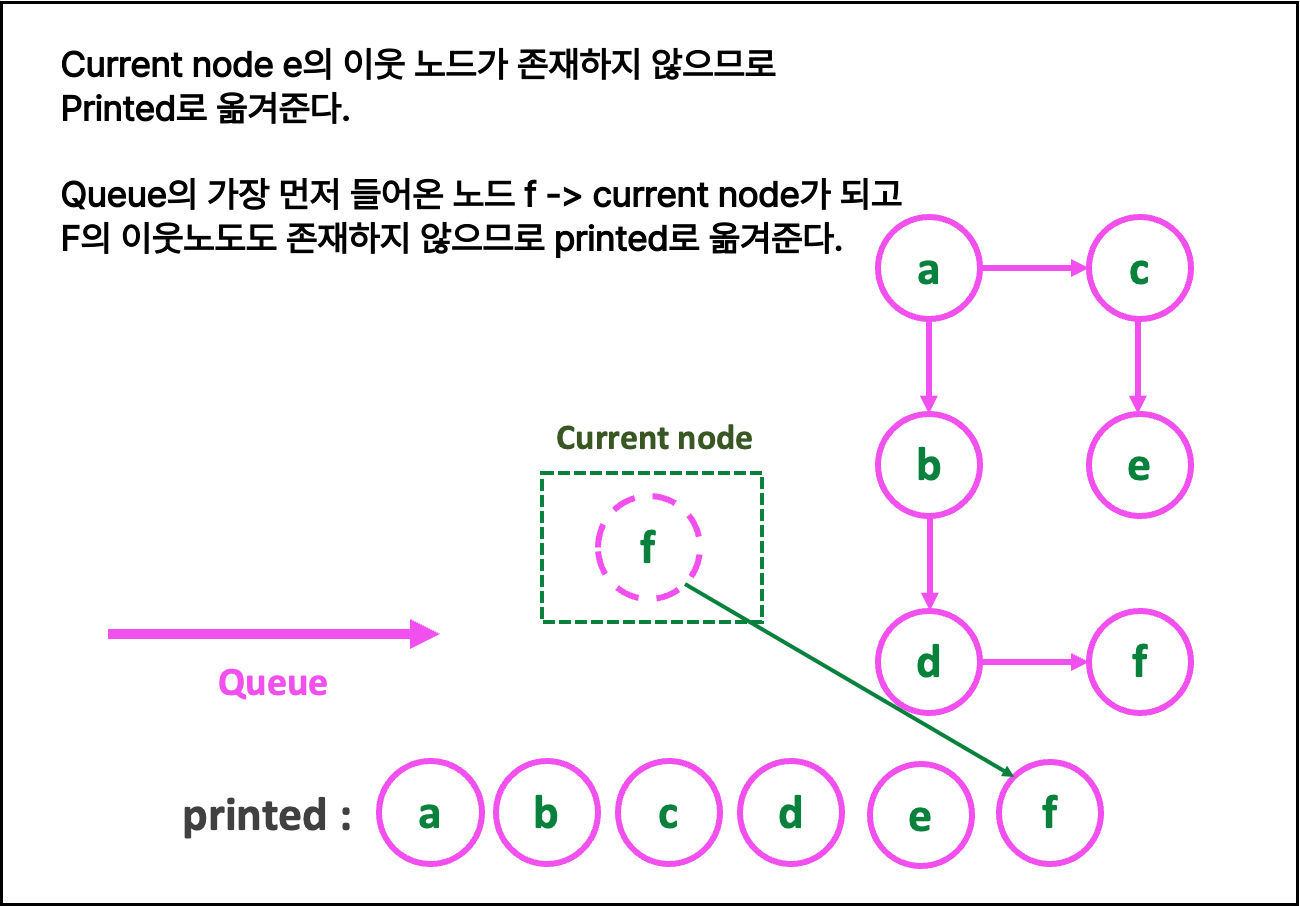
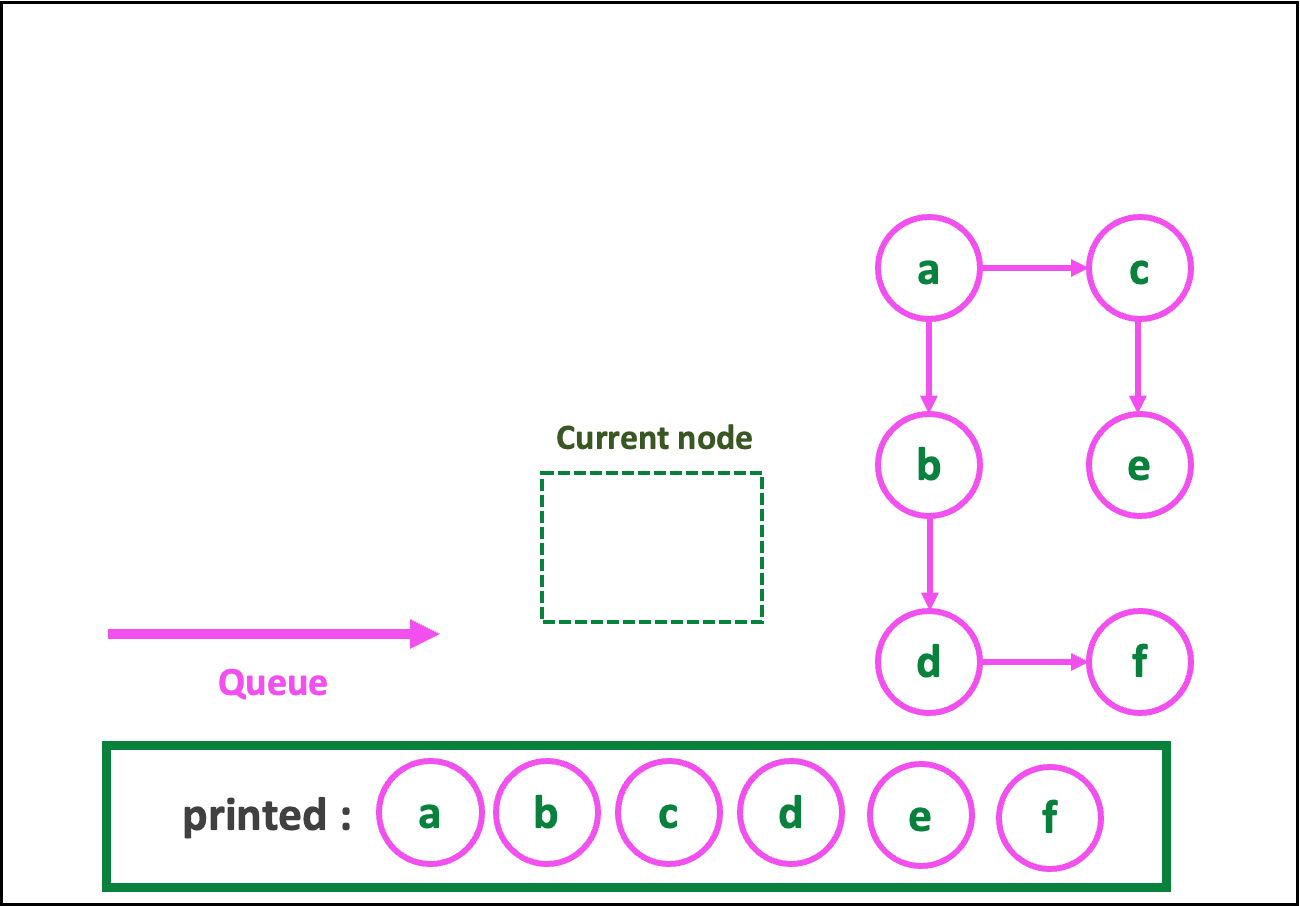
2. 글로 쓰는 로직
def BST(graph : 그래프, start_node : 순회 시작 노드)
필요한 자료구조 : queue=[], current_node, printed=[]
1. queue에 start_node 넣어주기
[ while(True) 반복문 : queue.empty() 일 경우 종료 ]
2. current_node = queue.get() 으로 해준다.
3. queue 에 current_node의 neighbors를 삽입
4. printed에 current_node를 append(추가)
3. 코드 구현
from queue import Queue
def bfsTraversal(graph, start_node):
queue = Queue()
printed = []
queue.put(start_node)
while not queue.empty():
current_node = queue.get()
printed.append(current_node)
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
queue.put(neighbor)
return printed
graph = {'a':[],'b':[],'c':[],'d':[],'e':[],'f':[]}
edges = [['a','b'],['a','c'],['b','d'],['c','e'],['d','f']]
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
print(bfsTraversal(graph, 'a'))
# 출력 결과 : ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
https://github.com/Seeun-Lim/Algorithm
GitHub - Seeun-Lim/Algorithm: 알고리즘 공부하는 공간
알고리즘 공부하는 공간. Contribute to Seeun-Lim/Algorithm development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'Python > [Algorithm] 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Q2:English] First and last index in sorted array (0) | 2022.06.02 |
|---|---|
| [Q1:Korean] Anagram, 철자 확인 (0) | 2022.06.02 |
| Binary Search, 이진 탐색 (0) | 2022.05.18 |
| DFS & BFS (3) : 노드 탐색 (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| DFS & BFS (2) : 경로 탐색 (0) | 2022.04.28 |
