👇🏻 출처
2022.04.28 - [Python/[Algorithm] 알고리즘] - DFS & BFS (2) : 경로 탐색
DFS & BFS (2) : 경로 탐색
🔹 출처 더보기 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tWVWeAqZ0WU 2022.04.26 - [Python/[Algorithm] 알고리즘] - DFS & BFS, 깊이 우선 탐색과 넓이 우선 탐색 (1) DFS & BFS, 깊이 우선 탐색과 넓이 우선 탐색 (1)..
sennieworld.tistory.com

{ 무방향 그래프 사이클 개수 찾기 }
위의 그래프에 연결되어 있는 노드의 집합은 {1,2}, {4,5,6,7,8}, {3} 으로 3개 이다.
🍍 { DFS : 깊이 우선 탐색 }
1. { 그림으로 살펴보기 }

노드 5~8은 이미 방문한 노드이므로 탐색하지 않는다.
2. { 구현 알고리즘 }
def cycleCount(graph, nodes: 노드 집합):
필요한 자료구조 : count=0, visited=[]
[ for 반복문 : 노드 집합에 있는 노드 순차적 탐색 ]
1. node가 visited에 있는 경우 (이미 방문한 노드), 넘어간다.
2. DFS를 할 stack을 만들고 stack에 node를 추가한다.
3. 방문한 노드에도 node를 추가하고, 사이클을 돌 준비가 됬으므로 count 를 하나 올려준다.
4. DFS로 노드의 이웃 노드들을 탐색한다. 만약, 이웃 노드가 visited에 있으면, 넘어간다.(사이클 안에서 도는 거 방지)
5. count를 반환한다.
3. { 구현 }
👇🏻 로직 그대로 구현한 Dirty Code
def findNode(graph,nodes):
count = 0
visited = []
for node in nodes:
if node in visited: continue
stack = []
stack.append(node)
visited.append(node)
count += 1
while len(stack)!=0:
current_node = stack.pop()
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
visited.append(neighbor)
stack.append(neighbor)
return count
nodes=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
edges = [[1,2],[4,6],[5,6],[6,7],[6,8]]
graph = {}
for node in nodes:
graph[node] = []
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
print(findNode(graph, nodes))
👇🏻 정돈된 clean 코드 ( 재귀 함수 )
def cycleCount(graph, nodes):
count = 0
visited =[]
for node in nodes:
if DFS(graph, node, visited) == True:
count+=1
return count
def DFS(graph, node, visited):
if node in visited: return False
visited.append(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
DFS(graph, neighbor, visited)
return True
nodes=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
edges = [[1,2],[4,6],[5,6],[6,7],[6,8]]
graph = {}
for node in nodes:
graph[node] = []
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
print(cycleCount(graph, nodes)) # 3

{ 가장 큰 사이클의 크기 찾기 }
위의 그래프에서 사이클의 크기(한 사이클의 노드의 개수)는 각각 4, 3이므로, 가장 큰 사이클의 크기는 4이다.
1. { 그림으로 정리하기 }

2. { 알고리즘 로직 }
def largestCycleSize(graph, nodes):
필요한 자료구조 : largest=0, visited=[]
1. 노드 집합에 있는 노드를 순차적으로 방문한다.
2. 노드가 visited 안에 있을 경우는 넘긴다.
3. 그렇지 않으면, size=1로 두고 DFS 탐색을 통해 이웃 노드를 visited에 넣어주고 size를 하나씩 증가시킨다.
4. largest와 size 비교 후 size가 클 경우, largest=size로 설정한다.
5. largest를 반환한다.
3. { 구현 }
👇🏻 알고리즘 로직대로 작성한 더티코드
def largestCycle(graph, nodes):
largest = 0
visited = []
for node in nodes:
if node in visited: continue
size = 1
stack = []
visited.append(node)
stack.append(node)
while len(stack) != 0:
current_node = stack.pop()
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
size+=1
visited.append(neighbor)
stack.append(neighbor)
if size>largest:
largest=size
return largest
nodes=[0,1,2,3,4,5,8]
edges = [[0,1],[0,5],[0,8],[2,4],[2,3],[3,4],[5,8]]
graph = {}
for node in nodes:
graph[node] = []
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
print(largestCycle(graph, nodes))
👇🏻 클린 코드
def largestCycle(graph, nodes):
largest = 0
visited=[]
for node in nodes:
size = exploreSize(graph, node, visited)
if size > largest: largest = size
return largest
def exploreSize(graph, node, visited):
if node in visited: return 0
size = 1
visited.append(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
size += exploreSize(graph, neighbor, visited)
return size
nodes=[0,1,2,3,4,5,8]
edges = [[0,1],[0,5],[0,8],[2,4],[2,3],[3,4],[5,8]]
graph = {}
for node in nodes:
graph[node] = []
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
print(largestCycle(graph, nodes))
{ 최단 거리 찾기 }
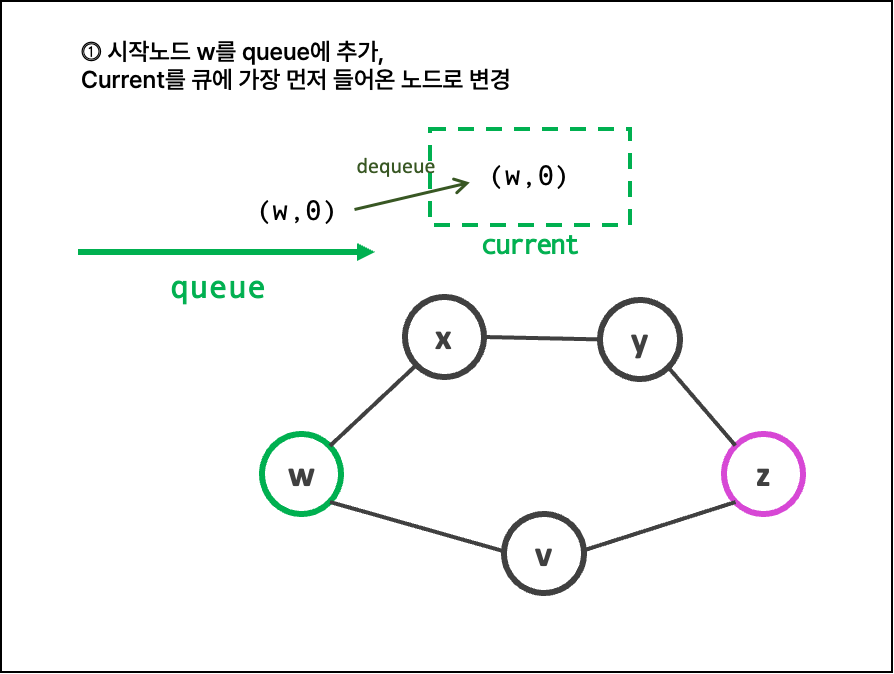
w에서 z까지 가는 경로는 [w->v->z] , [w->x->y->z] 이렇게 두 가지이고 각각 간선의 개수는 2, 3개이다.
간선의 개수를 거리라고 칠 때, w에서 z까지 가는 최단 경로는 2가 된다.
1. { 그림으로 살펴보기 }
최단 거리를 찾는데에, dfs와 bfs 중 어떤 방식을 사용할 것인지를 고민해보면 아래의 그림이 도움이 된다.
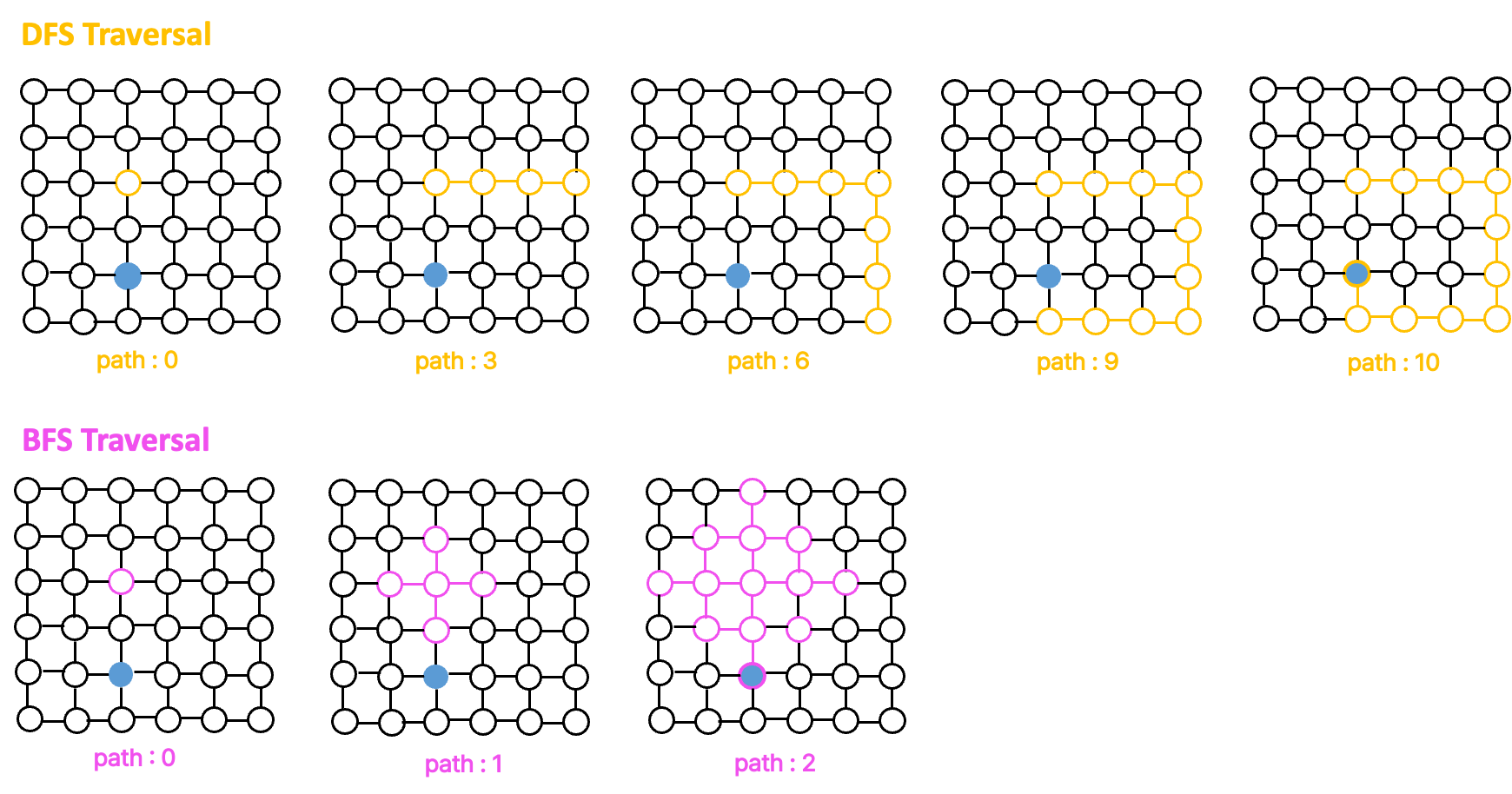
BFS의 path가 압도적으로 적은 것을 볼 수 있다.
🎀 : { BFS : 넓이 우선 탐색 }
queue에 (node, path) 형식으로 저장한다.



3. { 구현 }
from queue import Queue
def shortestPath(graph, src, dst):
queue = Queue()
visited=[]
queue.put([src,0])
while not queue.empty():
[current_node, current_path] = queue.get()
if current_node == dst:
return current_path
visited.append(current_node)
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
visited.append(neighbor)
queue.put([neighbor, current_path+1])
return False
nodes=['w','x','y','z','v']
edges = [['w','x'],['x','y'],['y','z'],['w','v'],['v','z']]
graph = {}
for node in nodes:
graph[node] = []
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
print(shortestPath(graph, 'w','z')) # 2
👇🏻 전체 코드 확인
https://github.com/Seeun-Lim/Algorithm
GitHub - Seeun-Lim/Algorithm: 알고리즘 공부하는 공간
알고리즘 공부하는 공간. Contribute to Seeun-Lim/Algorithm development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'Python > [Algorithm] 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Q2:English] First and last index in sorted array (0) | 2022.06.02 |
|---|---|
| [Q1:Korean] Anagram, 철자 확인 (0) | 2022.06.02 |
| Binary Search, 이진 탐색 (0) | 2022.05.18 |
| DFS & BFS (2) : 경로 탐색 (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| DFS & BFS (1) : 그래프 순회 (0) | 2022.04.26 |
